Knowledge Graph – Semantic Knowledge Base
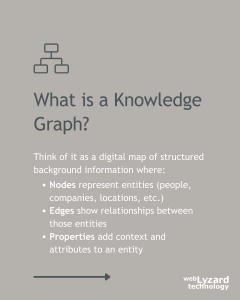
What is a Knowledge Graph?
A knowledge graph is a dynamic data structure to organize information in a way that both humans and machines can easily understand. At their core, they are digital maps that connect entities, their attributes, and the relations between them. Even though knowledge graphs have existed as a concept since at least the 1980s, they have recently seen a renaissance thanks to Generative AI and the desire to build explainable AI systems. In such systems, knowledge graphs structure relations while large language models (LLM) process and communicate them in human language. Thereby, knowledge graphs improve the explainability and accountability of AI while translating complex data into clear strategic insights.
How does webLyzard use Knowledge Graphs?
The Semantic Knowledge Base (SKB) of webLyzard is an evolving knowledge graph that integrates and aligns factual and linguistic knowledge from a wide range of domains into a single linked data graph. Tools for provenance management and access control facilitate its integration into a wide range of business and research applications. Many of these applications are time-critical. This challenge is addressed through a query abstraction and caching layer based on ElasticSearch. This distributed caching mechanism mitigates the performance bottlenecks of RDF triplestores and leads to radically reduced response times. It also allows us to provide a highly scalable Application Programming Interface (API). Through this API, our customers can build powerful and responsive business solutions with minimal effort.
Knowledge Graph Applications and Evolution
The webLyzard Knowledge Graph drives most Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. This includes entity annotation tasks, for example, as well as sentiment analysis and more fine-grained emotion detection. It also is a crucial part of the query engine of the visual analytics dashboard.
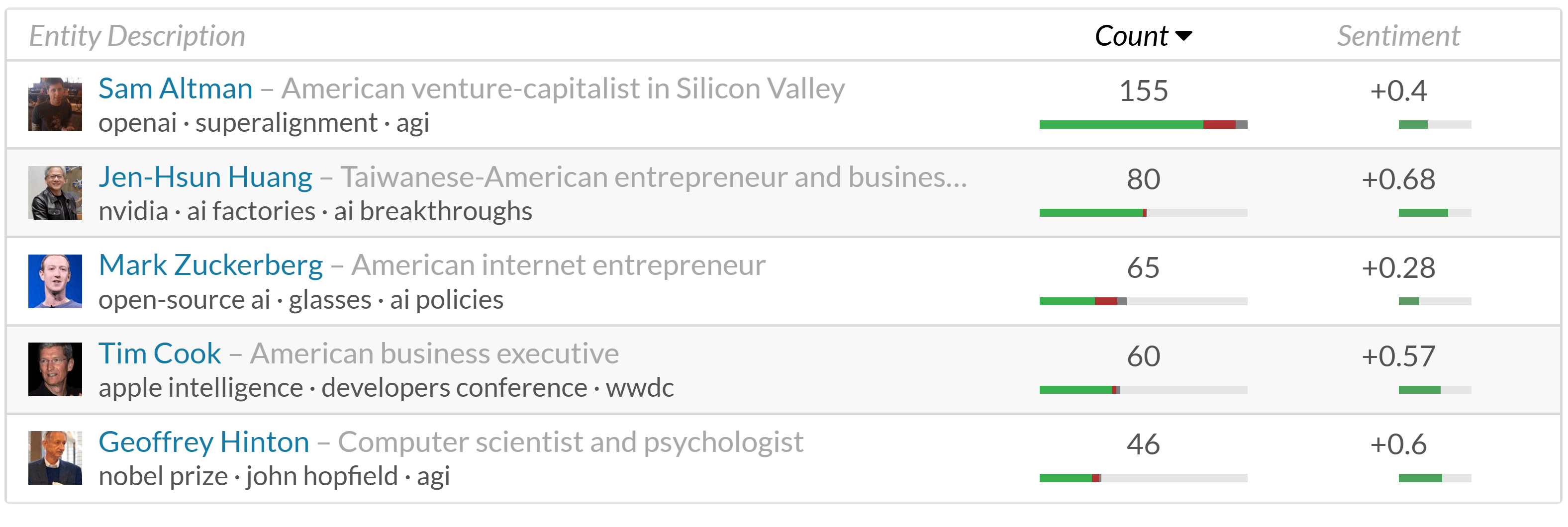
Opinion Leaders for the Search Query “Artificial Intelligence”
Factual knowledge is derived from external and internal sources. Initially, we process Linked Open Data (LOD) sources such as Wikidata for organizations or persons and Geonames for locations. Our in-house information extraction pipeline then suggests new entity types such as events and anniversaries. To disambiguate these entities, the graph also contains linguistic knowledge such as spelling and syntactic variations and multilingual translations.
State-of-the-Art Artificial Intelligence (AI) methods require large corpora for training purposes. Creating these corpora benefits from our team’s extensive experience in automated content analysis and media listening. As a result, the Knowledge Graph currently stores over 2.5 million entities. And it is still growing, currently at a rate of about 500 entities per day.
Semantic Knowledge Base Editor
To interactively access and modify the entities of the Knowledge Graph, the SKB Editor provides an intuitive visual user interface for our customers and research partners. The embedded search supports a variety of filter options. Selecting an entity tile in the search results shows the entity’s metadata properties. This includes language-specific labels, descriptions, alternate names and image thumbnails. The role-based access control provides a safe and efficient way to specify and update all aspects of the Knowledge Graph. It is also straightforward to restrict confidential information to a particular use case.
SKB Editor – Query for UN Organizations
Knowledge Graphs for Human-Centered Explanation
Explainable AI is key to achieving a human-centered and ethical development of digital solutions. The ENEXA Horizon Europe project builds on promising results in knowledge representation and machine learning to develop scalable, transparent and explainable ML algorithms for knowledge graphs. The focus on knowledge graphs acknowledges their critical role as enablers of novel digital solutions across European domains and industries.
The project’s approach to human-centered explanation will adopt the concept of co-construction, where humans and machines enter a conversation to jointly produce human-understandable explanations. The envisioned use cases include geospatial intelligence and data-driven brand communication. Given their expected growth rates, these sectors are going to play a major role in future European data value chains.